Classify jobs and maintain separate queues for each class.
Each queue can have its own scheduling algorithm.
Two examples of ways of choosing processes from the queues:
- Take jobs from the highest priority non-empty queue.
- Time slice among queues: each queue get a fixed share of the CPU time.
Examples of methods of assigning priorities:
- foreground vs. background
- batch vs. real time
- student vs. administrative
Allow jobs to change priority (and therefore their queue) dynamically.
To specify such a system you must specify:
- The number of queues
- The scheduling algorithm for each queue
- An initial queue assignment algorithm
- An upgrade priority algorithm
- A downgrade priority algorithm
VAX VMS Scheduling
The VAX uses a multi-level feedback queue system with 32 priority levels:
- 16-31 are static real-time queues.
They are scheduled according to priorities on a pre-emptive basis.
A process is assigned a priority when it starts and that determines its queue. - 0-15 are dynamic queues.
All processes from a given queue are executed before processes from any lower number queue is considered.
This is non -preemptive except for the quantum. - Each system call has a priority increment.
When an event occurs which causes a process to become executable, its priority is computed as the sum of the base and the increment. - Each time a process is scheduled its priority is decremented, but not below the base.
- Processes also age if they spend a long time in a queue.
This allows them to increase their priority.
Windows NT Scheduling (also W2000, XP, maybe Vista)
Similar to the VAX (since it was designed by the VMS designers)
- Processes waiting for keyboard or mouse get largest priority increment.
- The foreground process in the current window get a larger quantum.
- Scheduling is preemptive even on the dynamic queues.
Traditional UNIX Scheduling Algorithm UNIX 4.3 uses multilevel feedback queues.
- Each runnable process is assigned a number that determines which queue they are placed in.
- Lower numbers mean higher priority.
Negative numbers are for system processes which cannot be killed by signals. - First process in lowest nonempty queue is run.
You can nice to reduce your priority. - Time quantum of 0.1 second is used, and priorities are recalculated once a second.
- No preemption except for quantum expiration.
- Under some flavors of Unix, an interactive process running in a window that has the focus is given a higher priority.
- The process's user-mode priority is:
pusrpri = PUSER + .25 pcpu + 2 pnice
here pcpu is incremented each time the system clock ticks and the process is found to be executing.
It is also adjusted once per second for ready processes using a digital decay filter.
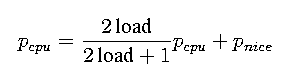
where load is the sampled average length of the run queue over the previous 1-minute interval of system operation. - When a process is blocked for an event, it cannot accumulate CPU time.
When a process has been sleeping for longer than 1 second
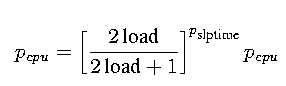
where pslptime is an estimate of how long its been blocked and load is the current system load - System does not preempt processes executing in kernel mode. This means it is not good for real-time system.
Linux Scheduling Algorithm
Linux Scheduling
This uses two separate process scheduling algorithms:
one for time-sharing which concentrates on fairness, and
one for real-time tasks where absolute priorities are more important.
Time sharing processes based on a credit system.
Each process has a fixed priority and a variable number of credits.
- When a new task must be chosen, the one with the most credits is run.
- Every time the timer interrupt occurs, the running process loses one credit and is removed from the CPU when its credits run out.
- If no runnable process has any credits, the credits of all processes
in the system are adjusted using the formula:
credits = credits/2 + priority
- What does this do if left to run?
- Can this starve out processes?
- the highest priority real-time task is run first
- only if there are no runnable real-time tasks will a time-sharing task run.
- for tasks of the same priority it is FCFS
- if scheduling class is FCFS, will run until it requests I/O
- real-time processes do not preempt other processes
Next Notes
Back to CS 3733 Notes Table of Contents