CS 2213 Advanced Programming
Heap Sort
Overview
The heap sort is an efficient sort which is easy to implement.
It is order n log n in worst case.
Compare this with the quicksort which is order n log n on average
but order n*n in the worst case.
Idea: use a binary tree.
- Step 1:
Put the numbers is a binary tree called a heap.
A heap is a binary tree in which the parent is at least as large as any of
its children.
Note: This implies that the largest value is at the root.
- Step 2
Sort the tree so that traversal by levels, left to right, will go from smallest
to the largest.
Now the smallest value is at the root.
Step 1: Creating the Heap
Assume that the values are available one at a time.
We insert one node at a time, retaining the heap property.
A tree with one node is always a heap.
Suppose we have a heap of size k and we want to add a node
to form a heap of size k+1.
- Insert the node as the last leaf of the tree.
- Do the following while possible:
If the parent has a smaller value, interchange with the parent.
- This process is called trickle up.
Consider the following example: 23, 42, 74, 11, 65, 58, 94, 36, 99, 87
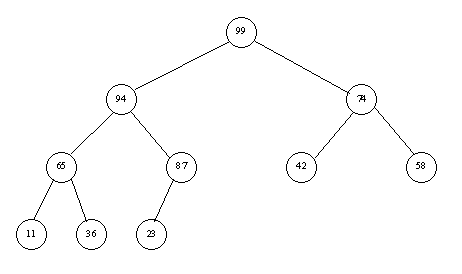
Step 2: Sorting the Heap
Idea: We know the root is the largest value.
Suppose we have a heap of size k.
Interchange the root with the last node.
The last node is now in the correct position.
We now almost have a heap of size k-1 but the root is in the
wrong position.
If the root is smaller than one if its children, trickle the root down,
interchanging it with its larger of its children.
Continue this until we have a heap of size k-1.
Continue this process.
Consider the example above.
Implementation
The implementation is very simple if we use an array to represent the tree.
We store the array by levels.
Consider an array:
int vals[MAXSIZE];
for storing a tree of size n with n > 0 and n <= MAXSIZE.
vals[0] holds the root.
vals[1] holds the left child and vals[2]holds the right child.
On the next level we have the left child of vals[1] in vals[3]
and the right child in vals[4].
The children of vals[2] are in vals[5] and vals[6].
In general, the children of A[k} are A[2k+1] and
A[2k+2]
The parent of A[k] is A[(k-1)/2], where integer arithmetic is
used for truncation.
Implementation Details
Here are some methods that you might use to implement a heap sort:
void insertOneInHeap(int vals[], int k);
Assume vals[0] ... vals[k-1] already a heap.
Make vals[0] ... vals[k] a heap.
void makeHeap(int vals[], int size);
Call insertOneInHeap in a loop:
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
void sortHeapOne(int vals[], int k);
Assume vals[0] ... vals[k] a heap,
interchange root and position k and make
vals[0] ... vals[k-1] a heap by trickling down the root.
This is the only hard one.
You must make sure that you do not access the array past postion
k.
void sortHeap(int vals[], int size);
Assume vals[0] ... vals[size-1] is a heap.
Sort it by calling sortHeapOne in a loop (backwards).
void printTree(int vals[], int size);
Print the tree in a nice readable format.
This one is for debugging.
int checkSorted(int vals[], int size);
Return true if sorted, false otherwise.
This one is for debugging.
void getRandomArray(int vals[], int size);
Set vals to a random array.
This one is for debugging.

