Objectives
- Prepare for Final
- Common Final Information
- You can review two sample final exams here and here
- You can find some additional review problems here
- You will be given a sheet of standard methods you can refer to during the exam.
You can see a copy of this sheet here.
Assignments
- Lab 9 Due Beginning of Week 15
- Project 3 Due
- Final
Final Review Problems 1
Material to Review
For Java programming, review the labs, the projects, and the activities from the lecture notes. Some of these will likely be part of the exam.For general knowledge, review Chapters 1-5, Sections 7.1-7.4, Supplement 3G, your quizzes, and the lecture notes. Understanding the chapter summaries and self-check problems is a good way to start reviewing the book material. Below is a table of particular items to pay attention to:
| Reading | Chapter Summary | Self-Check Problems |
|---|---|---|
| Chapter 1 | Everything | 6, 9, 12, 14, 16, 18-19, 22-25 |
| Chapter 2 | Everything | 1-2, 6-7, 11-12, 16, 19-20, 23, 26-27, 32 |
| Chapter 3 | Everything | 5-6, 10, 13-14, 16, 20-21, 24, 26 |
| Supplement 3G | Everything | 3-4 |
| Chapter 4 | Everything except System.out.printf | 1-2, 5-7, 9, 16, 20, 26-27 |
| Chapter 5 | Everything except do/while | 1-2, 4-5, 12-13, 14-15, 17, 23 |
| Chapter 7 | Everything except multidimensional arrays | 2, 4-5, 9-10, 15-17, 19, 29 |
Note: All the Self-Check Problems are good to do. The above selects a subset of them as examples of what to study.
Lists of Terminology, Notation, and Keywords
Terminology
Hover mouse for more information
|
|
|
Notation
Hover mouse for more information
|
|
|
|
|
Keywords
Hover mouse for more information
|
|
|
|
Final Review Problems 2
Final Review Problems 3
Additional Activities
Activity: Draw Red and Blue Circles
Write a Java program that draws the following pattern on a DrawingPanel:
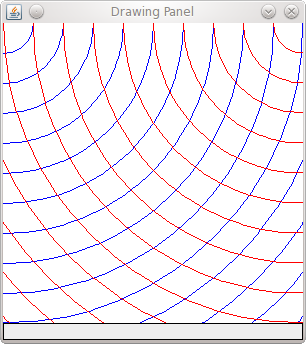 Hint: Draw blue circles centered at (0,0) and red circles
centered at (300,0).
Hint: Draw blue circles centered at (0,0) and red circles
centered at (300,0).
Write a Java program that draws the following pattern on a DrawingPanel:

Activity: Three Doubles Mehtods
Write a Java program that inputs three doubles from the user. Write and test methods for one or more of the following tasks.
Write a Java program that inputs three doubles from the user. Write and test methods for one or more of the following tasks.
-
Return the mininum of the three numbers.
Write one version using Math.min and another version using if statements.
[See Self-Check Problem 16 in Chapter 3.] - Return the median of the three numbers.
- Return true if all three numbers are equal to each other.
- Return true if all three numbers are different from each other.
- Return true if two of the three numbers are negative.
Activity: Determine Data Type
Write a Java program that inputs a token from the user and determines whether the user entered an int, double, or a String. Hint: Use the hasNextInt and hasNextDouble methods of Scanner. [See the ExamineInput1 program on p. 345.]
Write a Java program that inputs a token from the user and determines whether the user entered an int, double, or a String. Hint: Use the hasNextInt and hasNextDouble methods of Scanner. [See the ExamineInput1 program on p. 345.]
Activity: StringAgain
Write a Java program that inputs Strings from the user until the user enters the first String again.
Answer:
What will be the difference if the nextLine method is used instead of the next method?
Some variations on this task include:
Write a Java program that inputs Strings from the user until the user enters the first String again.
Answer:
import java.util.*;
public class StringAgain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the first string:");
String first = console.next();
String next = ""; // priming the loop
while (! first.equals(next)) {
System.out.print("Enter the next string:");
next = console.next();
}
}
}
What will be the difference if the nextLine method is used instead of the next method?
Some variations on this task include:
- Write a Java program that inputs Strings from the user until the user enters a different String.
- Write a Java program that inputs Strings from the user until the user enters a String that contains a 'z'.
- Write a Java program that inputs Strings from the user until the user enters the same String twice in a row.
Activty: Divisible by 2
Write a Java program that inputs an int from the user and determines how many times the number is divisible by 2. The program should keep dividing the number by 2 until the number is odd. [See Self-Check Problem 4 in Chapter 5.]
Write a Java program that inputs an int from the user and determines how many times the number is divisible by 2. The program should keep dividing the number by 2 until the number is odd. [See Self-Check Problem 4 in Chapter 5.]
Activty: Double Array Methods
Write a Java program to input doubles from the user for an array.
First ask the user how long the array should be.
[See the Temperature2 program on p. 450.]
Write and test methods for one or more of the following tasks.
Write a Java program to input doubles from the user for an array.
First ask the user how long the array should be.
[See the Temperature2 program on p. 450.]
Write and test methods for one or more of the following tasks.
-
Return the sum of the array.
Answer:
public static double sumArray(double[] list) { double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { sum += list[i]; } return sum; }
- Return the maximum element of the array. [See Self-Check Problem 10 in Chapter 7.]
- Increment every element in the array. [See p. 454 and p. 477.]
- Replace negative elements with zeroes.
- Return the number of elements that are negative.
-
Return true if every element is negative.
Answer:
public static boolean allNegative(double[] data) { int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) { if (data[i] < 0) { count++; } } return (count == data.length); }
This code serves as a hint for the previous and next tasks in this list. - Return true if most of the elements are negative.
Activity: Self Check 29
This is based on Self-Check Problem 29 in Chapter 7.
Write a method that computes the average String length of an array of Strings. For example, the array {"Write", "a", "method", "in", "Java"} has an average length of 3.6. Write a Java program that tests your method.
This is based on Self-Check Problem 29 in Chapter 7.
Write a method that computes the average String length of an array of Strings. For example, the array {"Write", "a", "method", "in", "Java"} has an average length of 3.6. Write a Java program that tests your method.