One way around this is to use a linked list for all of the entries corresponding to a given hash function value.
The hash table becomes an array of pointers to linked lists.
Consider a hash table "object" with the following hashtable.h file:
typedef struct stringval {
char *str;
int val;
} stringval;
/* Return a hash table initialized to empty. */
int hashinit(int size);
/* Insert sval into the hashtable htp.
Return 1 on success and 0 on failure. */
int hashinsert(stringval sval);
/* Remove sval from the hashtable htp.
Return 1 on success and 0 on failure. */
int hashremove(stringval sval);
/* Return a pointer to the entry for str in the hashtable htp.
Return NULL if not found. */
stringval *hashfind(char *str);
Notice that in this description, all implementation issues are hidden from the
user.
The implementation we will look at has the hashtable as an array of pointers to linked entries:
typedef struct hashentry {
stringval sval;
strcut hashentry *next;
}hashentry;
We can use a modified version of the hash function as before:
static int hashsize;
static int hashfunction(char *str) {
unsigned int hashval;
int i;
hashval = 0;
for (i=0;str[i]!=0;i++)
hashval = 37*hashval + str[i];
return hashval % hashsize;
}
Now we can write the 4 public methods:
int hashinit(int size); int hashinsert(stringval sval); int hashremove(stringval sval); stringval *hashfind(char *str);
Here is the code we wrote in class:
int hashinit(int size){
hashsize = size;
htp = (hashentry**)malloc(sizeof(hashentry *)*hashsize);
int i;
if (htp == NULL)
return 0;
for (i = 0; i < hashsize; i++)
htp[i] = NULL;
return 1;
}
int hashinsert(stringval sval) {
int hashval;
hashentry* nentry;
hashval = hashfunction(sval.str);
if (hashfind(sval.str) != NULL)
return 0;
nentry = (hashentry *)malloc(size of(hashentry));
if (nentry == NULL)
return 0;
nentry -> sval = sval;
nentry -> next = htp[hashval];
htp[hashval] = nentry;
return 1;
}
The class ended here.
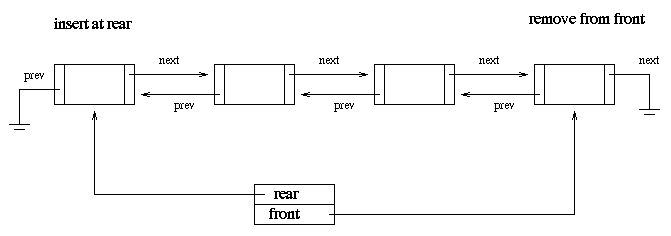
Practice with doubly linked lists:
typedef struct nodeentry {
stringval sval;
struct nodeentry *next;
struct nodeentry *prev;
} nodeentry;
typedef struct {
nodeentry *front;
nodeentry *rear;
} doublelist;

int insert_after(stringval sval, nodeentry *nentryp); int insert_before(stringval sval, nodeentry *nentryp); stringval remove(nodeentry *nentryp);